Drinking Health: Polyphenols & Flavonoids

Health Benefits of Tea
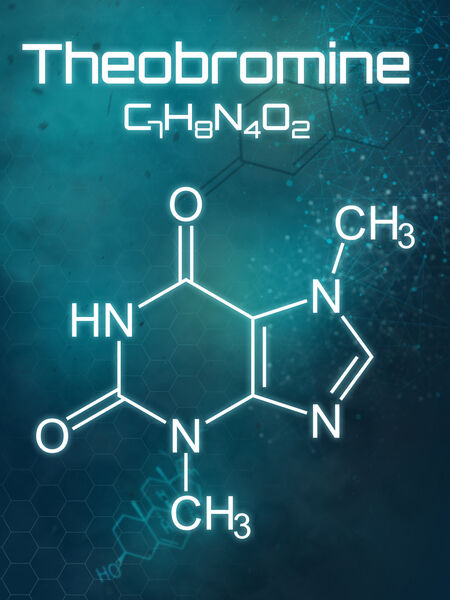
One of the great advantages of drinking tea over coffee is the presence of various xanthines which offer a two-punch benefit: they stimulate the brain while they relax the body. Xanthines and methyl-xanthines are 62 different stimulants found only in plant foods. The most common is caffeine, which is in chocolate, cola, coffee, and to a minor degree, in tea. But tea boasts other xanthines, such as theine and theobromine. These xanthines, while chemically similar to caffeine, are metabolized more slowly in the human body, which tends to create a milder, longer effect with less of a "crash" than caffeine.
Disease-Fighting Polyphenols
Another benefit in tea is its high quantities of polyphenols, the "pac men" that literally eat away at free radicals which cause cancerous tumors to grow, allow disease to spread, and cause medical havoc in our bodies. The more foods and beverages containing polyphenols we consume, the better chances our bodies have of fighting off free radicals.
Free radicals are oxidants that are unstable molecules that damage cells, change DNA and cause disease. Therefore, antioxidants like polyphenols are needed to fight cellular damage and repair cell damage. Because many diseases are the result of cellular damage, polyphenol activity through the consumption of tea can be a vital benefit in any healthful diet.
All tea, whether it has been processed (oxidized) or not, contains healthful and beneficial polyphenols. White and green teas, because they are not oxidized, may contain higher amounts. Polyphenols have been shown to improve the status of oxidative stress biomarkers (the predictors of disease risk). Understanding how these antioxidant workhorses work is the next learning curve for scientists. Studies have shown promising evidence that polyphenols may help us fight cardiovascular diseases, cancers, osteoporosis, diabetes mellitus, and some neurodegenerative diseases and may enhance overall bone and dental health.
Health-Giving Flavonoids
Polyphenols contain phytochemical compounds called flavonoids that provide antioxidant activity and tannins that contribute to the flavor of the tea, most particularly its astringency. Catechins, a higher level of one type of flavonoids, appears in very small amounts in oxidized tea and in substantial amounts in green teas and a little less in white teas. Catechins are considered potent antioxidants and hold the most promise for fighting heart disease and cancer. Catechins appear in small quantities in grapes and wine, chocolate, and all types of tea from Camellia sinensis. The abundant catechins in teas, especially green teas, are divided into seven different categories: catechin, epicatechin (EC), epigallocatechin (EGC), epicatechin gallate (ECG), gallocatechin (GC), gallocatechin gallate (GCG), and epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). These are among the leading plant-derived molecules scientists are studying for their potential health benefits for everything from arthritis to cancer to cardiovascular disease.
 teaclass
teaclass
